Extrapolating UK's oil production history to the World case
Posted by Chris Vernon on May 15, 2006 - 5:49pm in The Oil Drum: Europe
Roberto makes some very interesting observations about UK North Sea oil extraction, article below.

Click to enlarge.
- Both have a premature and clear peak (World in 1980 and UK in 1985). The absolute peak for the UK was in 1999. Although the world probably hasn't done its absolute peak yet it will soon.
- The premature peak on both cases had a non-geological component: in the World case it was the Iran-Iraq War and the OPEC embargo, and in the UK case the PIPER accident.
But there were also geological reasons for the decline: in the World case the fields in South Arabia were probably overproduced until 1980 (see "Twilight in the Desert"), and in the UK case Brent's production collapsed after 1988 (but after 3 or 4 years new technology like horizontal drilling came to the rescue and gave new life to the field, hat tip to MUDLOGGER).
- As in the rest of the Oil basins of the world, in the UK there is a King (Forties, which production started in 1975), Queen I (Brent 1976), Queen II (Ninian 1978), and a few Lords (Magnus 1983, Piper 1976 & Nelson 1994).

Click to enlarge.Clearly, the giant fields in the UK were discovered very quickly. In the World case, most of the super-giants were also discovered quite early in the oil history (and the few exception like the Cantarell field are bound for big declines real soon).
- Actually, the premature peak of UK is quite well explained by these premature discoveries. I will try to show this by the following graph:

Click to enlarge.So the production of UK without its biggest 5 oilfields is very Gaussian-like or Hubbert-like. This trend continues, that is, if you remove the 18 oilfields that had average production over 50 thousand barrels a day, you get an even smoother profile:

Click to enlarge.Still a bump between 1975 and 1993 remains, that is because between 1975 and 1984, another 25 fields were discovered with considerable average production rates.
I claim that the world case has a similar behaviour, i.e. if you leave out the super-giants you obtain a Gaussian-like or Hubbert-like curve.
In summary, I think that the premature discoveries of super-giants can cause odd production profiles. So it would be better to factor them out before you do modeling.
Also note that the role of very mature super-giants won't be decisive in the future, since their weight in the overall production will diminish. This is very clear in the case of UK, where nowadays Forties, Brent, Ninian, Magnus & Piper represent just a small portion of the total production.
One more picture of UK's oil production:

Click to enlarge

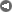



I have to admit that I am not as convinced by Hubbert Linearization as I was before. I am planning to post a comment soon about my criticisms of the Hubbert Linearization method. Basically the Hubbert Linearization method makes almost everything look like a line. Hubbert Linearization method plots cumulative production versus (real production)/(cumulative prod) and then a Hubbert curve gets transformed into a line. But if you plot cumulative versus real production the Hubbert curve gets transformed into a parabola that passes through the origin.
See Jean Laherrère (pages 11-14)
for some graphs of this type. I think that this method is much more reliable and robust to determine the peak.
We tested the reliability of the HL model regarding the Lower 48 in the following article: http://www.energybulletin.net/13575.html
I do have a suggestion for an experiement of sorts. It is remarkably easy to do an HL plot for the North Sea using the EIA data. It would be interesting to see what kind of Qt that several people came up with. Data (crude + condensate): http://www.eia.doe.gov/emeu/ipsr/t41b.xls
Jeffrey J. Brown
westexas@aol.com